Brain Mapping
What is Brain Mapping? QEEG (Quantitative Electroencephalogram) or Brain Mapping is an essential diagnostic procedure used in evaluating ADD/ADHD, Autism, Learning Disorders, Anxiety, and Depression. It tells us if the symptoms are neurologically based. If neurologically caused, then there is a high probability of treatment success using a Neurofeedback treatment program.
QEEG (Quantitative Electroencephalogram) or Brain Mapping is an essential diagnostic procedure used in evaluating ADD/ADHD, Autism, Learning Disorders, Anxiety, and Depression. It tells us if the symptoms are neurologically based. If neurologically caused, then there is a high probability of treatment success using a Neurofeedback treatment program.
19 sensors are placed on the surface of the head, according to a system of clinical EEG standards, and brain wave activity is recorded over those 19 areas. It is noninvasive and painless. Much like a thermometer which only records your temperature but does not affect your temperature, the Brainmap only records the electrical activity of the brain; it does not do anything to the brain.
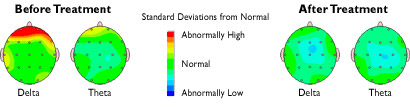
The Brain Mapping will detect if any area of the brain is malfunctioning or misfiring. The patient's brainmap is processed and compared to a "normative database." This means that your brainmap is compared to that of a group of normal people your age and sex.
We know in general what cognitive or emotional functions each area of the brain performs. If one or more of the locations shows reduced activity (either from too many slow brain waves or not enough fast brain waves), then we can predict what type of symptoms the patient may be experiencing as a result of that area malfunctioning. For example, if the frontal region of the brain shows excessive slow brainwaves and the patient has attentional difficulties, then we have a "match" to help him/her with a Neurofeedback protocol to train the frontal lobes to regulate more normally.
As another example, the right temporal region is involved in emotional regulation, so if it is malfunctioning, we would expect the child to have difficulty with emotional regulation or frustration tolerance. Again, here we can help this child with Neurofeedback to normalize this region to improve emotional regulation.
EEG is a diagnostic approach, very similar to a physician doing a throat culture on a patient with a sore throat and fever to determine which antibiotic would best eradicate the infection. Without a QEEG, a clinician cannot truly know if the symptoms are neurologically based, or simply psychological/behavioral. If neurological, the Brainmap pinpoints which brainwaves are abnormal and which location. Neurofeedback treatment can then be based on these findings.
Scientific Studies on QEEG Brain Mapping and ADD/ADHD: (pdf format)
» Society of Biological Psychiatry: Inhibition in Children with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder:
A Psychophysiological Study of the Stop Task
» Clinical Neurophysiology: EEG evidence for a new conceptualisation of attention deficit
hyperactivity disorder
» International Journal of Psychophysiology: Simultaneous EEG and EDA measures in adolescent
attention deficit hyperactivity disorder
» Psychiatry Research: Excess beta activity in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder:
an atypical electrophysiological group
What to Expect:
An EEG is a painless, non-invasive diagnostic test which monitors the ever present and ongoing electrical activity in the brain. Brain waves are amplified and the signals are fed to a computer, saved on the hard drive, and later retrieved for visual and computer analyses. The EEG can be used to detect epileptic or other abnormal brain activity.
A QEEG is a BRAINMAP. It is a quantitative computer analysis of the raw EEG. It determines the amount (power) of the different frequency bands of the EEG (delta, theta, alpha, beta) and determines the coherence (relationship) between these bands. Coherence is a measure of connectivity between the various brain areas. The patient's data is then statistically compared with the data from a group of individuals the same age who are normal (a normal data base). The BRAINMAP is then used to guide neurofeedback training. If a given feature is quantitatively more in the patient than in the controls (normal data base), that feature is "downtrained," i.e., the patient is trained with neurofeedback, to make less of it. If a given feature is lower than in the normal group, it is "uptrained," i.e., the patient is trained to make more of it. The goal is to normalize the QEEG patterns, which in turn normalizes the functions and connections of the brain, resulting in remediation of the patient's symptoms. A BRAINMAP is also useful as a diagnostic tool for head injury, addictions, learning disabilities, autism, ADHD, anxiety, depression and other neurological conditions. When requested, an experienced board certified M.D. Neurologist can provide a report for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes based upon the QEEG data.
To perform both the EEG and the QEEG a cap with 19 built-in sensors, covering the head, is placed on the patient's head. These sensors are surface electrodes that make contact with the patient's head, plus one on each ear lobe. A saline-based gel is added to each electrode to enhance the recording. Once all connections are made and checked, the collection of data begins. This consists of two to four different sections. The sections with eyes closed, eyes open and reading should each take about seven minutes each. If a child is too young to read this recording is not done. When epilepsy is involved or suspected, a fourth strobe light section is included. This section takes about three minutes during which it is very important for the patient to keep his/her eyes closed for about three minutes. The entire procedure takes about an hour and is divided almost equally between setup and the actual test recording.
In order to ensure accurate results, the patient should relax, breathe normally, remain quiet, still, and follow instructions. An irregular heartbeat, sweating, eye movement, eye blinking, muscle tension, sucking movements, chewing, or any movement can cause inaccurate results.
After the necessary reports are generated and analyzed, the office will call the patient to make an appointment with Dr. Peters to explain and discuss the results.
To prepare for an EEG or a QEEG:
» Make sure you are rested and not sleep deprived the night before the test.
» Avoid foods or beverages that contain caffeine.
» Make sure your hair is clean and free of any hair sprays, creams, or gels.
» Avoid excessive make-up on the face.
» Remove any hair accessories.
» Eat before being tested.
» Try to achieve a degree of relaxation before the test.
» Please turn off cell phones to minimize distractions.
Take all prescribed medications unless instructed otherwise. Please ask if you are in doubt. Approximately 1 1/2 hr is allocated for this diagnostic test. In order to be fair to other patients, you are requested to be on time for your appointment. Please allow extra time if you have to do paper work or fill out forms.
